Posts by saranas
Comparison of a Pure Plug-Based Versus a Primary Suture-Based Vascular Closure Device Strategy for Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: The CHOICE-CLOSURE Randomized Clinical Trial
Saranas Wins InnovationMap Inaugural Award For the Healthcare Business Category
The votes are in — and it’s time to announce the winners of the inaugural InnovationMap Awards, presented by Techwave.
Baird Capital’s Venture Team Leads $12.8MM Series B Investment in Saranas
Today, Saranas, Inc. announced a $12.8 million Series B investment led by Baird Capital, the venture capital and global private equity arm of Baird. Baird Capital was joined in the investment by Austin, Texas-based S3 Ventures.
Trends, Predictors, and Outcomes of Major Bleeding After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation, From National Inpatient Sample (2011-2018)
Utilizing Adjunctive Technologies For Same-Day Discharge Post TAVR
Philippe Généreux, MD – Morristown Medical Center
Background
- Patients undergoing TAVR procedures may be candidates for early or same-day discharge if certain criteria are met including no intraprocedural bleeding complications1.
- COVID-19 has resulted in a surge of ICU admissions that has stressed ICU resources within hospital systems, limiting bed capacity.
- Providers seek objective metrics to confirm safety of patient disposition for early discharge.
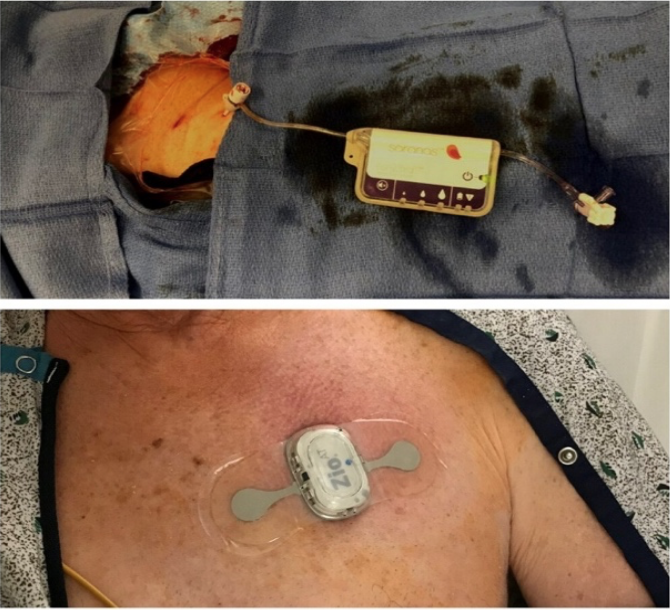
- The Early Bird® Bleed Monitoring System provides assurance to clinicians that no intra and post- procedural bleeding events occur for a patient vulnerable to bleeding complications.
- The Zio® (iRhythm® Technologies, Inc.) is a wearable heart monitor that attaches to the patient’s chest for a period of up to 14 days.
Case
- 69-year-old male
- TAVR procedure incorporating the Zio patch and the Early Bird
- Patient is a candidate for same-day discharge given that there is no detection of bleeding by the Early Bird
Results
- Following successful TAVR procedure, the Early Bird remained activated for post-procedure monitoring.
- With no identified procedural complications and no bleed notifications from the Early Bird, the patient was safely discharged on the same day.
- The Zio patch remained on the patient for 2 weeks to monitor conduction disturbances.
- The patient was out on the golf course 2 days following the procedure.
Discussion Points
Integration of adjunctive technologies, such as the Early Bird and Zio, may make early or same-day discharge following a TAVR procedure feasible.
Incorporation of a risk-stratified same-day discharge TAVR algorithm has the potential to ease patient disposition and satisfaction, while reducing hospital resource utilization and ICU burden.
1 Généreux P et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 87:980-982, 2016.